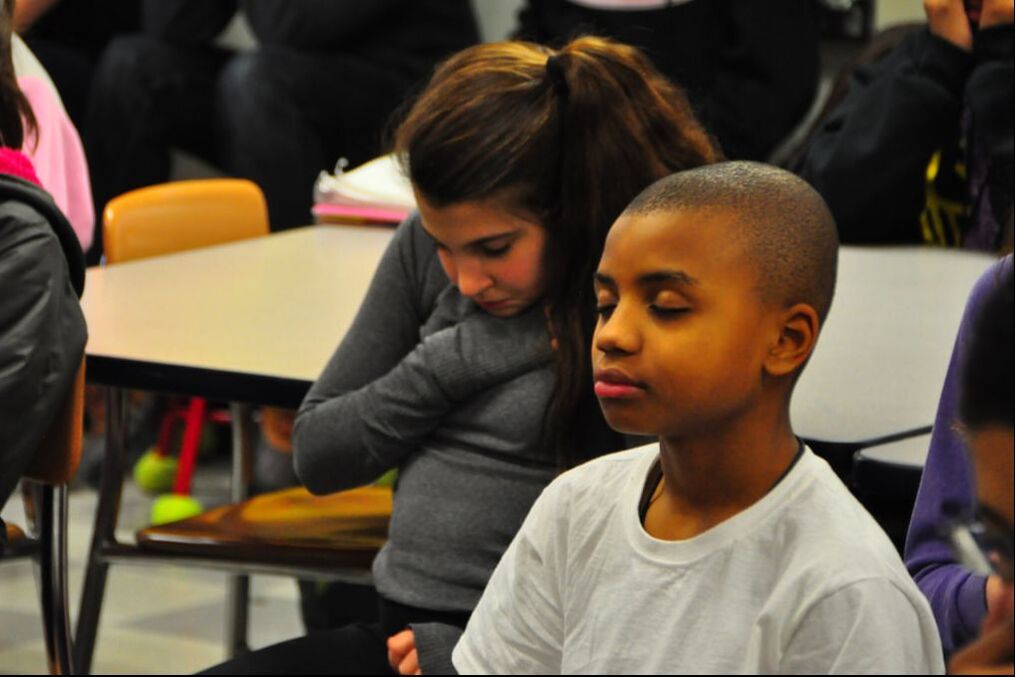
Students assigned to participate in the mindfulness intervention received eight weeks of daily mindfulness instruction for a total of 24 hours of instruction while the active control group of students received training in a computer coding curriculum designed to teach creative thinking, reason and collaboration for a similar duration.
Students assigned to the mindfulness intervention condition showed a significant reduction in perceived stress and but no difference in the affect measures when compared to the active controls. Since right amygdala changes were found to be associated with greater fear responses, investigators also assessed brain changes in this area. Significantly lower amygdala activation was found for the mindfulness trained group in comparison to the controls. These students also showed significantly increased functional connectivity between brain regions (amygdala-ventromedial prefrontal cortex) associated with emotional regulation than the control group. These findings suggest the potential value of mindfulness interventions for alleviating stress, as reflected in both the subjective report and objective measures. Comments are closed.
|
Categories
All
Archives
July 2024
|
Make a difference.
|
Copyright © 2020 Michigan Collaborative for Mindfulness in Education


 RSS Feed
RSS Feed